|
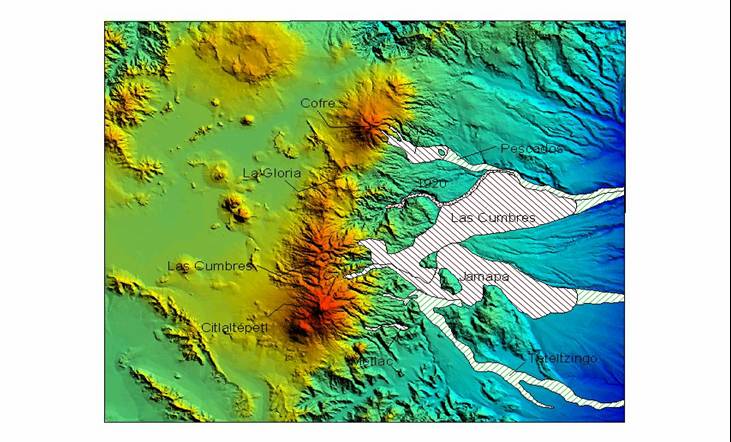
Distribution of
main deposits derived from multiple collapsing events at the
Citlaltépetl-Cofre de Perote volcanic range. All directed to the east (Gulf
od Mexico). The abrupt eastward drop in relief between the Altiplano (west)
and the Gulf of Mexico (east)
provinces gives rise to unstable conditions and consequent
gravitational collapse of large volcanic edifices built at the edge of the
Altiplano like Citlaltépetl, Las Cumbres, and Cofre de Perote. There have also
been several small-scale landslides and debris flows in Holocene times, some
of which are not related to the activity of the large volcanoes (e.g. the
1920 seismogenic event). There are also a few isolated exposures of other
volcaniclastic deposits, but their sources remain unknown. Some of the
resulting avalanches and transformed flows have exceptionally long runouts
and reach the Gulf of Mexico after traveling more than 120 km from their
source, mainly as hyperconcentrated flows (not shown in this figure).
|