Modeling phosphorous loads to the Great Lakes under future land use
and climatic conditions
|
|
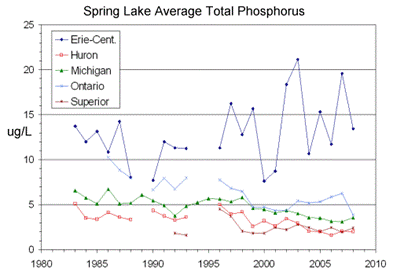
Phosphorous (P) loads are responsible for increases in algal
bloom in the Great Lakes over the last decade. We assess the vulnerability of
watersheds in the basin towards contributing P loads in the context of
changes in land use and climate. We
use statistical and deterministic modeling approaches. First, plausible scenarios for expansion of urban and
agricultural areas over a 30-year period are generated. Land uses are
converted to P source terms, which are input to a calibrated model of P fate
and transport. Predictions of P loads emanating from the watersheds to the
Great Lakes are generated. Watersheds are assessed according to their
capacity to attenuate P sources, which is related to land surface properties
and hydraulic residence times. |
Seasonally-varying, nonlinear regressions between P loads and
discharges are fitted to observations. Climate forcings for near- and
far-future periods are input to watershed-scale hydrologic models to predict
changes in discharges and corresponding P loads. The vulnerability of
watersheds to seasonal changes and corresponding P loads varies significantly
across the basin.
|
Presentations
·
2014 AGU poster on
phosphorous loads and climate variability and change
·
2011 International Association of Great Lakes Research talk on phosphorus
loads and land use change
Papers
Collaborators
·
Veronica Griffis, Michigan
Tech
·
Dale Robertson, USGS Madison, Wisconsin
·
David Dempsey, International Joint
Commission
·
David Saad, USGS Madison,
Wisconsin
Funding sources
·
NSF Water Sustainability and Climate planning grant