Applications of AVHRR data to
Global Change Research
The goal of this document is to describe the proceedure to process AVHRR data, and to
provide examples of processed data.
Characteristics of the AVHRR Sensor
 Average Orbital Height: 830 km (515 Miles)
Average Orbital Height: 830 km (515 Miles)
 Spatial Resolution:
Spatial Resolution:
- Global Area Coverage (GAC): 4.4 kilometers
- Local Area Coverage (LAC): 1.1 kilometers (Available over the U.S. and in some parts of the world)
 Swath Width: 2800 kilometeres
Swath Width: 2800 kilometeres
 Coverage: 2 times per day per satellite
Coverage: 2 times per day per satellite
 Records Data in 5 Wavelength Intervals
(bands)
Records Data in 5 Wavelength Intervals
(bands)
- Visible Green and Red (0.58 to 0.68 microns)
- Near Infrared (0.72 to 1.10 microns)
- Mid Infrared (3.53 to 3.93 microns)
- Thermal Infrared (10.3 to 11.3 microns)
- Thermal Infrared (11.5 to 12.5 microns)
 Bands 1 and 2 record reflected energy
Bands 1 and 2 record reflected energy
 Band 3 records reflected energy during
the day and emitted energy at night.
Band 3 records reflected energy during
the day and emitted energy at night.
 Bands 4 and 5 records emitted thermal (heat)
energy
Bands 4 and 5 records emitted thermal (heat)
energy
Geographic Coverage
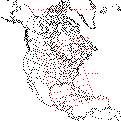
The image above shows AVHRR coverage on January 4, 1995 at 00:30 GMT (Eastern time is GMT
-5 hours). The satellite was moving from southeast to
northwest (ie. ascending). The horizontal lines are at one minute increments.
Geographic Rectification and Registration
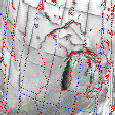
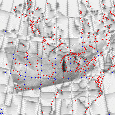
As the satellite passes over the earth, it scans the surface beneath it at an angle of +/- 63
degrees. As a result, the spatial resolution varies from 1.1 km directly beneath the satellite,
to 5.5 km at the edge of the swath. This causes geometric distortions to occur. The image on the
left shows an example of the unrectified data. In our processing, we use an automated
routine that utilizes satellite tracking information to determine where the satellite was when it
acquired the data. Once the position of the satellite is known, the data can be registered to
and earth location. This registered data, can then be rectified to any map projection. The image
on the right is the rectified version of the image shown on the left. Note that this is the
same data shown in the example of geographic coverage shown above.
AVHRR Sensor Calibration
Before the data can be used in a quantitative manner, it needs to be calibrated.
The calibration algorithm is based on information contained
in the
Polar Orbitor User's Guide. Briefly, the visible and near infrared
data (channels 1 and 2) are converted from raw counts to
percent albedo using a linear relationship determined prior
to launch. The thermal infrared data (channels 3, 4, and 5)
are converted from raw counts to radiances with a linear
relationship that is based on the raw count value associated
with cold space (roughly 3 degrees Kelvin) and the raw count
value associated with the temperature of an onboard target
(approximately 300 degrees Kelvin). A slight nonlinearity
in channels 4 and 5 is corrected using a quadratic function
of radiance. Lastly, the infrared radiances are converted
to temperature using the inverse Planck function.
Examples of the Use of AVHRR Data
 Volcanic Eruption Clouds
Volcanic Eruption Clouds
 Lake Superior
Lake Superior
 Global Vegitation Composite
Global Vegitation Composite
 Sea Surface Temperature Archive-URI
Sea Surface Temperature Archive-URI
Ordering Data
The Satellite Active Archive (SAA) is a system designed to provide easy access to data from
NOAA's satellites. SAA contains descriptive information about those data sets, and permits users
to search inventories of data holdings for availability based upon geographic and date requirements.
In addition to providing advanced online data query and product request capabilities, SAA also
provides an online graphical browse tool which can assist the user in determining geographic
coverage of individual data sets and display online digital representations of those data sets. Once
the data requirements have been determined an order may be placed electronically, and data may
be delivered either electronically or through physical medium.
 NOAA Satellite Act
ive Archive
NOAA Satellite Act
ive Archive
The Pathfinder AVHRR Land data sets are global, multichannel, land surface data derived from the
Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometers (AVHRR) on the NOAA/TIROS operational
meteorological satellites (NOAA-7, -9, and -11) which provide a continuous daily and composite
data set from July 1981 through the present. These data, when complete, will enable studies of
global vegetation and surface characteristics over more than a decade. Every effort has been made
to provide a consistently processed data record by cross-calibrating instruments and minimizing
changes to the processing algorithm during the processing of the 1981 to present data.
 NOAA/NASA AVHRR Pathfinder Home Page
NOAA/NASA AVHRR Pathfinder Home Page
Technical Information
An online version of the Polar Orbitor User's Guide. This document gives you many of the details
about the sensors, data structure, processed products, and placing orders.
 Polar Orbitor User's Guide
Polar Orbitor User's Guide
 Average Orbital Height: 830 km (515 Miles)
Average Orbital Height: 830 km (515 Miles)
 Spatial Resolution:
Spatial Resolution:
 Swath Width: 2800 kilometeres
Swath Width: 2800 kilometeres
 Coverage: 2 times per day per satellite
Coverage: 2 times per day per satellite
 Records Data in 5 Wavelength Intervals
(bands)
Records Data in 5 Wavelength Intervals
(bands) Bands 1 and 2 record reflected energy
Bands 1 and 2 record reflected energy
 Band 3 records reflected energy during
the day and emitted energy at night.
Band 3 records reflected energy during
the day and emitted energy at night.
 Bands 4 and 5 records emitted thermal (heat)
energy
Bands 4 and 5 records emitted thermal (heat)
energy

