In a stunning display of ‘when it rains, it pours,’ Dr. Simon Carn, a Professor at the Department of GMES, has bagged two prestigious awards within a month—a feat as rare as spotting a double rainbow. On April 5, Dr. Carn was honored with the Michigan Tech Research Award, recognizing his outstanding achievements in research. Just weeks later, on April 18, he was bestowed the title of Distinguished Professor, an accolade awarded to faculty members who have made substantial contributions to the University and their discipline.
Dr. Carn has made seminal contributions to both applied and fundamental aspects of volcanology, remote sensing, and meteorology. Recognized as a world authority on multi-sensor remote sensing of volcanic clouds, he uniquely blends advanced knowledge of remote sensing, volcanology, and atmospheric science. His research is noted for its innovation, collaborative spirit, and versatility, focusing on employing remote sensing data in studies of volcanic degassing, eruption clouds, and anthropogenic pollution. Dr. Carn excels in translating theoretical understanding into practical solutions, significantly impacting volcanic hazard prediction and mitigation and enhancing aviation safety. This blend of academic and practical prowess has earned him broad international recognition, including the American Meteorological Society Special Award and the NASA/US DOI William T. Pecora Award.
Dr. Carn has secured substantial external funding to support his research, with contributions from prestigious agencies such as NASA, NSF, and NOAA, underscoring the scientific community’s strong confidence in his work. His external expenditure ranks among the highest at MTU. His scholarly output is both prolific and collaborative, featuring 133 peer-reviewed publications and book chapters, many co-authored with his students. He is also among the most cited researchers at the university.
An inspiring mentor and instructor, Dr. Carn has guided four postdoctoral researchers, 22 PhD and 36 MS students. He led our successful dual International Master in Geology (INVOGE) program from 2009 to 2015 in collaboration with Université Blaise Pascal, the University of Buffalo, and the University of Milan Bicocca. His students have found employment in the public, government, and academia worldwide.
Dr. Carn has made significant contributions to his professional community, serving as an Associate Editor for the Journal of Geophysical Research and as Secretary of the Remote Sensing Commission of the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth’s Interior (IAVCEI) since 2008. Additionally, he has been a member of the National Academy of Sciences Committee on Improving Understanding of Volcanic Eruptions, the AAAS Review Committee for the U.S. Geological Survey Volcanic Hazards Program, and various scientific committees for international conferences and workshops.
Importantly, Dr. Carn has been very active and efficient in outreach and promotion of science. He is a frequent and long-term contributor to NASA’s Earth Observatory educational website and other outlets such as Scientific American and National Geographic. He conducted TV, radio, and newspaper interviews with BBC World Service, The Weather Channel, Wall Street Journal, Weather Underground, and others. Finally, he has actively promoted his research on X (formerly Twitter) with more than 7000 followers as of today.
Congratulations, Simon, on these well-deserved awards!

Simon Carn (GMES) was quoted by NASA Earth Observatory in a story about an eruption of the La Cumbre volcano in the Galápagos islands. The eruption began March 2 on Fernandina Island, and the story included a March 7 aerial image showing continued active lava flow.
“This is typical of lava-producing effusive eruptions, which usually show peak emissions early on followed by a steady decline towards the end of the eruption.”
Carn’s research includes using satellite measurements to constrain global volcanic SO2 production and emissions from individual volcanoes.

The AggCelerate student team from the Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences (GMES) has advanced to the top six nationally in Phase 2 of the Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration (SME)/National Stone, Sand, and Gravel Association (NSSGA) Student Design Competition. The annual competition is a grueling two-phase, team-based, problem-solving activity involving a technical design and an oral presentation.
Under the guidance of Dr. Nathan Manser, Professor of Practice at GMES, the team has demonstrated exceptional skill and knowledge in their field.
The team members, listed in alphabetical order, are:
- Cassie Burch (Junior, Geological Engineering)
- Aiden Harmon (Junior, Mining Engineering)
- Lucas Maxon (Sophomore, Mining Engineering)
- Ian Repic (Senior, Mining Engineering)
- Nathan Seidel (Senior, Mining Engineering)
- Grady Williams (Junior, Mining Engineering)
During Spring break, the team will participate in the second phase during the 2024 SME Annual Conference and Expo. Michigan Tech will be competing against runner-up teams from the University of Kentucky, Virginia Tech, University of Arizona, West Virginia University, and Missouri University of Science and Technology.
In the second phase of the competition, students have one weekend to solve a design problem and present their findings to a panel of judges. The competition is designed to simulate an engineering project prepared by an engineering group for a company. Past problems have highlighted the challenges of mine planning, plant design, reserve modeling and feasibility analysis.
This year’s sponsors of the SME/NSSGA Student Design Competition are:
- Executive sponsor: Glacier Resource Estimation Group/Costmine
- Title sponsors: Granite Construction, National Stone, Sand & Gravel Association (NSSGA) and Luck Stone
- Supporting sponsors: New Enterprise Stone & Lime Co. Inc. and Carter Machinery
Shiliang Wu (GMES/CEGE) was quoted by Planet Detroit in a story explaining how a winter atmospheric inversion lowered air quality January 7-8, 2024, in Detroit. Wu co-authored a 2016 study that found a 50% increase over the last 60 years in the frequency of winter atmospheric inversions and summer heatwaves, which can both increase air pollution. The story was picked up by Great Lakes Now.
“For the last at least 60 years we have data for, we can clearly see a trend of increasing temperature inversions in mid-latitude regions.”
Wu is a dual-appointment professor in Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences and Civil, Environmental, and Geospatial Engineering. His research involves impacts of global change on atmospheric chemistry and long-range transport of air pollution.
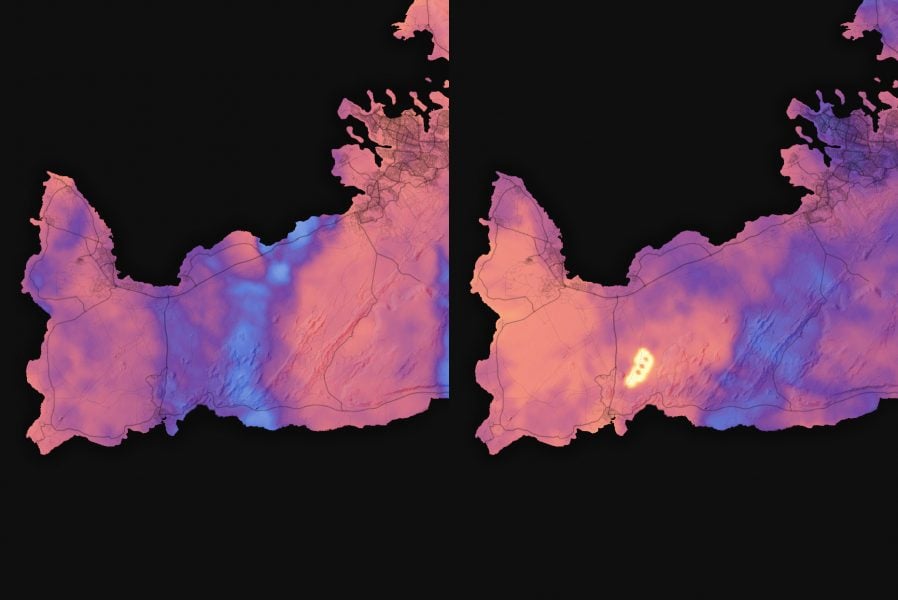
Simon Carn (GMES) was quoted by NASA’s Earth Observatory in a story about the eruption of lava from a new fissure on Iceland’s Reykjanes Peninsula, which began late on Dec. 18. Carn interpreted a brightness temperature image comparison of the eruption area between Dec. 18 and 19, and commented on the reported risk to nearby infrastructure.
“If lava continues to flow north, it could eventually reach the key main road from Keflavík airport to Reykjavík.”
Carn’s current research focus is the application of remote sensing data to studies of volcanic degassing, volcanic eruption clouds, and anthropogenic pollution.
The Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences is pleased to award five bachelor’s, and two master’s degrees this December.
Two graduate degrees awarded:
Breen, Dillon MS Geology
Advised by Dr. Luke Bowman
Metts, Isabella MS Geophysics
Advised by Dr. Greg Waite
Five undergraduate degrees awarded:
Hawes, Jack W. BS Geological Engineering
Johnson, Samuel A. BS Geology
McClelland, Elliz E. BS Geology
Myaard, John S. BS Geological Engineering
Verran, Maria E. BS Mining Engineering
Congratulations, and best of luck on all future endeavors!
This summer, Elliz McClelland interned in the URISE (Undergraduate Research Internships in Seismology) program, funded by EarthScope (formerly known as IRIS). This internship experience gave them professional research experience, guidance about graduate schools, and the opportunity to work with an institution they’d like to work at during their career. As part of their internship experience, they will also present at the annual national American Geophysical Union (AGU) meeting in December 2023, a completely new experience for them.
During Elliz’s internship, they conducted research into a volcanic caldera using geophysics in New Mexico. Elliz worked under the mentorship of the United States Geological Survey and spent part of their summer working in the USGS office in Denver, Colorado. This internship was a multi-faceted experience where they had the opportunity to do a lot of traveling. Elliz spent their first couple of weeks performing fieldwork in New Mexico in their study area, then moved into Denver to work at the USGS office. They were also lucky enough to work on a separate USGS project where they traveled to Hawaii to help their mentor conduct field research. Their summer was full of new experiences and cultures!
The URISE internship was highly targeted toward providing research experience and preparation for graduate school. While Elliz intends on taking a least one gap year before attending graduate school, the information the internship coordinators provided them about graduate school was instrumental in making their decisions about furthering their education.
When reflecting on the value of the URISE internship, Elliz says, “For my needs, this internship was also immensely useful in determining my career path. I ‘put my boots on the ground’, so to speak, working directly with the USGS under a position I might like to hold myself in the future. My summer experience really confirmed for me that I love doing field work and I would enjoy working for an institution like the USGS.”
In December, Elliz presented their work at the AGU national conference in San Francisco, California. This conference is one of the biggest Earth Science conferences in the nation and is an excellent opportunity for students to meet potential employers, experience the professional research conference environment, and network with fellow geoscientists. For more details about Elliz’s internship experience and the research they conducted, you can visit their summer blog at URISE. Elliz would also like to highly recommend this internship to any geoscience students with an interest in research and geophysics. Anybody can apply and prior geophysics experience is not required! You can stay updated about internship applications at URISE.
Jacob T. Murchek presented his doctoral research proposal defense on Friday, December 1, 2023. Advised by Dr. James DeGraff, with Dr. Benjamin Drenth, Dr. Jeremy Shannon, and Dr. Aleksey Smirnov serving as committee members.

Title: Integration of Geophysical Data with Geologic Constraints to Infer Tectonomagmatic Controls on Mineral Systems in the Yukon-Tanana Uplands, Alaska, and Keweenaw Peninsula, Michigan
Abstract: Critical minerals are necessary for the everyday needs of modern human society and are paramount for the advancement of technology. Lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite are some examples of critical minerals used in cell phones, military equipment, vehicles, batteries, and other essential products. To increase domestic production of critical minerals, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) seeks to identify areas favorable to host deposits of such minerals through the Earth Mapping Resources Initiative. In collaboration with the USGS, the proposed research aims to identify tectonomagmatic controls of mineral systems in the Yukon-Tanana Uplands (YTU), Alaska, and along the Keweenaw Peninsula (KP), Michigan, using geophysical and geologic data to better understand the distribution and origin of such systems and to judge critical mineral potential in the two areas.
Both the YTU and KP have the potential to host critical mineral deposits, however, mineral systems in these areas are not completely understood. Critical minerals in the YTU are most likely to occur as secondary minerals associated with precious metal mineral systems. Aeromagnetic data will be interpreted, modeled, and integrated with regional geology, magnetic susceptibility measurements, and geochemical data to aid in delineating the boundary between the parautochthonous North American Basement (NAb) and allochthonous Yukon-Tanana Terrane (YTT) that underlie the YTU. Establishing a firm boundary for these terranes has major implications for understanding the origin and distribution of mineral systems across the YTU (e.g., porphyry Cu-Au, orogenic Au) and, consequently, the potential for such systems to host critical minerals. The research will emphasize developing geophysically mappable criteria for these and other mineral systems and the plutonic suites that may be associated with their deposition and enrichment. Along the KP copper district and its southwest extension, gravity and magnetic data, and possibly seismic reflection data, will be acquired to model the structure of the Midcontinent Rift System (MRS), thereby testing published cross-sectional models for the rift and the Keweenaw fault system (KFS). Better definition of the KFS is relevant to understanding migration pathways of copper-bearing hydrothermal fluids that produced economic deposits of copper and silver in the region. Quantitative geophysical modeling in the region can be tightly constrained by bedrock outcrops and rock property measurements (e.g., density, magnetic susceptibility). A better constrained subsurface model across the southeast margin of the MRS will establish a stronger tie to offshore geophysical data previously collected across Lake Superior. Such models should also improve the definition of known faults in the KFS as well as identify new faults beneath Jacobsville Sandstone, thus helping to infer mineralization pathways for copper and other elements associated with the MRS.
You are invited! The Department of Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences (GMES) is hosting an alumni social in conjunction with the MineXchange 2024 SME Annual Conference in Phoenix, AZ, from 5:30-7:30 PM on Tuesday, February 27, 2024, at the Sheraton Phoenix Downtown.
Plan to attend and network with MTU alumni from all facets of the SME community, plus take the time to meet the newest huskies as they embark on their professional careers in the industry.
Michigan Tech’s AggCelerate team, advised by Dr. Manser, has advanced to the top six nationally in the SME/NSSGA Student Design Competition. The second phase of the competition will take place during the SME Conference.
Michigan Tech will be competing against runner-up teams from the University of Kentucky, Virginia Tech, University of Arizona, West Virginia University, and Missouri University of Science and Technology. Student teams will have one weekend to solve a design problem and present their findings to a panel of judges. The competition is designed to simulate an engineering project prepared by an engineering group for a company.
Michigan Tech team members, listed in alphabetical order, are:
- Cassie Burch (Junior, Geological Engineering)
- Aiden Harmon (Junior, Mining Engineering)
- Lucas Maxon (Sophomore, Mining Engineering)
- Ian Repic (Senior, Mining Engineering)
- Nathan Seidel (Senior, Mining Engineering)
- Grady Williams (Junior, Mining Engineering)
Event and Student Travel sponsorship opportunities are available at this time for 2024 in Phoenix and 2025 in Denver; please contact Nathan Manser (ndmanser@mtu.edu) for more details.
Each year the Institute on Lake Superior Geology (ILSG) offers competitive funding for student research projects that focus on the geology of the Lake Superior region. This year, Braxton Murphy, a senior in geological engineering, was awarded $500 to support his project titled “Determine the Relative Paleostress State and Tectonic Conditions That Resulted in Formation and Movement of Faults of the Keweenaw Fault System near Houghton, Michigan.”
Braxton’s research with Jim DeGraff involves measuring slip indicators along the Hancock fault where it is exposed in the Quincy Mine workings and at a rock quarry near the town of South Range. These data will be analyzed to infer the paleostress state that caused faults in the Keweenaw fault system to move, thus allowing different ideas about the Midcontinent Rift System to be evaluated. Research activities in fall 2023 focused on the Hancock fault, and next year will focus on the South Range quarry.
Research findings will be presented at the 70th annual ILSG meeting to be held at Michigan Tech in May 2024.










